Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy?
We offer Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) as a form of psychotherapeutic treatment that has proven effective in addressing various mental health concerns. These include depression, anxiety disorders, addiction issues, emotional difficulties, and severe mental illnesses such as bipolar disorder, borderline personality disorder, eating disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder, schizophrenia, post-traumatic stress disorder, panic disorder, psychosis, and phobias. Extensive research indicates that CBT can lead to notable improvements in overall functioning and quality of life.

We found research indicating that Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) is a leading evidence-based treatment for eating disorders. Additionally, scientific studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of CBT in addressing insomnia and medical conditions that disrupt sleep. Moreover, CBT has also been proven beneficial in the treatment of depression and anxiety. In a 2018 meta-analysis of 41 studies, CBT was found to significantly improve symptoms in individuals with anxiety and anxiety-related disorders, including obsessive-compulsive disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder. An approach using CBT can help us enhance self-control, manage triggers, and develop coping mechanisms when dealing with addiction issues.
How does Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) work?
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy is a combination of cognitive and behavioural therapy to identify maladaptive patterns of thoughts, emotional responses, or behaviours. The goal of this approach will be to replace them with more rational patterns. Therapists focus on CBT to change irrational thoughts that contribute to emotional difficulties, depression, and anxiety. This structured therapeutic approach emphasizes our current life rather than solely focusing on underlying factors that led to the difficulties.
In the sessions, therapists help us to understand the role of thoughts, feelings, and situations in driving maladaptive behaviours. While the process of learning and identifying these distortions may be challenging, it leads to self-discovery and provides crucial insights for the treatment process. Therapists guide us in facing our fears and confronting negative distortions to bring about behavioural changes.
Furthermore, therapists equip us with problem-solving skills to effectively cope with difficult situations and foster a greater sense of confidence in our abilities. Therapists place particular emphasis on empowering us to become our own therapists by helping us to identify negative distortions, develop coping skills, and modify problematic thoughts, emotions, and behaviours.
How is Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) applied in session?
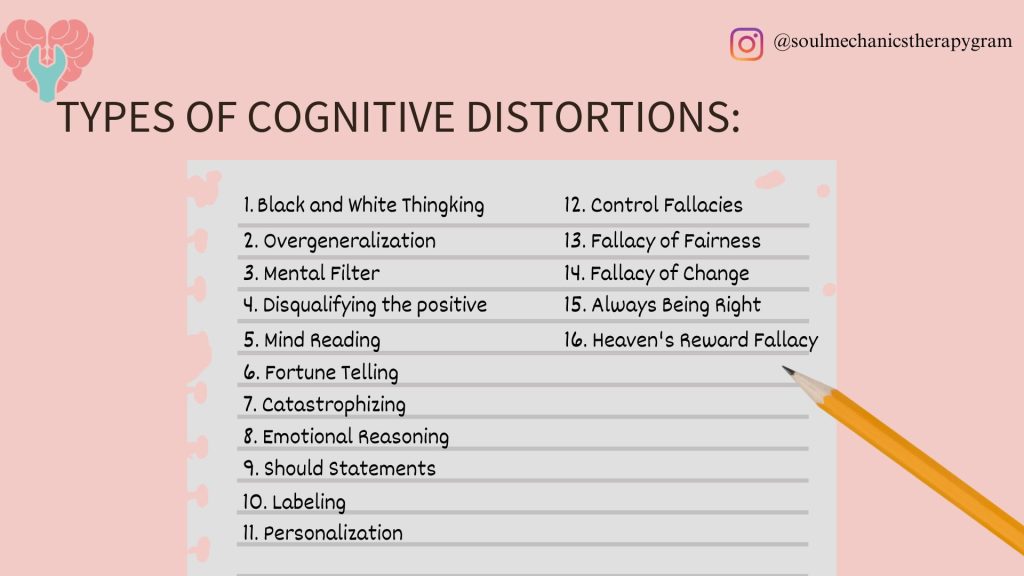
In therapy sessions, therapists work collaboratively with us to break down our challenges into specific components, including thoughts, feelings, and behaviours. Then, analyse these areas and identify the cognitive distortions such as:
1.0 Black and White Thinking
Inability or unwillingness to see the shades of grey. Only see things in the extreme, either perfect or a total failure.
2.0 Overgeneralization
Jump to a conclusion easily; Conclude with only a few attempts of experience.
3.0 Mental Filter
Similar to overgeneralization, jumping to a negative conclusion easily excludes all the positive outcomes. Only focus on the negative and ignore all the positive results.
4.0 Disqualifying the Positive
Acknowledge the positive results but disqualify them instead of embracing them. A malignant distortion that facilitates the continuation of the same patterns even when facing strong evidence to the contrary.
5.0 Mind Reading
Jumping to a negative interpretation of another person's thoughts. An inaccurate belief in reading others' minds and jumping to negative conclusions about oneself.
6.0 Fortune Telling
Similar to mind reading, a tendency to make conclusions and predictions with little or no evidence. Always predict the future with a negative outcome or something bad will happen.
7.0 Catastrophizing
Maximizing or minimizing the meaning, importance, and factor of an incident.
8.0 Emotional Reasoning
Belief and accept the emotion as fact although the emotion is just a feeling of oneself instead of the truth.
9.0 Should Statements
A tendency to make "should" statements, imposing expectations that are unlikely to be met.
10.0 Labelling
An extreme form of overgeneralization. Jumping to conclusions based on one instance or experience.
11.0 Personalization
Taking everything personally and self-blaming without logical reason.
12.0 Control Fallacies
A control fallacy manifests as one of the beliefs; I have no control over their lives, or I have complete control of everything.
13.0 Fallacy of Fairness
An assumption of an inherently fair world is not based on reality.
14.0 Fallacy of Change
A belief in expecting changes in others with pressure or encouragement to lead him/her to happiness and success rate.
15.0 Always Being Right
A belief of perfectionism that he/she must be right.
16.0 Heaven's reward fallacy
A belief that struggles, suffering, and hard work will result in a just reward.
Is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy helpful?
Similar to any counseling session, the session begins with the counselor exploring our issues, thoughts, feelings and behaviours. The therapist will be placing a great amount of emphasis on actively listening and acknowledging our concerns and emotions. As the counseling session progresses, our counselor will introduce and work collaboratively with us to identify any negative distortions within us. Furthermore, our counselor will be looking for relevant coping skills and practical strategies that can effectively address our concerns. Therefore, it is vital for us to remain committed to the process. This is to maximize the benefits that can be reaped from this therapeutic journey. In conclusion, attending sessions regularly and completing "homework" assignments. This is a must to help us grow and strengthen our coping skills.
Another interesting approach in therapy will be Psychodynamic Therapy, you can read more about it here.
For more content related to mental health do follow us on our official Instagram.

